library(tidyverse)这本书是哈德利的入门之作。虽然对于我来说有点过于简单,不过这本书是以系统的观点阐述数据分析中的各个问题,并且都是用tidyverse工具箱中的包解决的。利用闲暇时间读一遍能够系统学习一边tidyverse,也不算浪费时间。不过这本书过的速度可以稍微快一点,毕竟很多都是太基础的内容。
3. 数据可视化
ggplot2的基础语法
ggplot(data = <DATA>) +
<GEOM_FUNCTION>(
mapping = aes(<MAPPINGS>),
stat = <STAT>,
position = <POSITION>
) +
<COORDINATE_FUNCTION> +
<FACET_FUNCTION>样例数据:mpg
str(mpg)## Classes 'tbl_df', 'tbl' and 'data.frame': 234 obs. of 11 variables:
## $ manufacturer: chr "audi" "audi" "audi" "audi" ...
## $ model : chr "a4" "a4" "a4" "a4" ...
## $ displ : num 1.8 1.8 2 2 2.8 2.8 3.1 1.8 1.8 2 ...
## $ year : int 1999 1999 2008 2008 1999 1999 2008 1999 1999 2008 ...
## $ cyl : int 4 4 4 4 6 6 6 4 4 4 ...
## $ trans : chr "auto(l5)" "manual(m5)" "manual(m6)" "auto(av)" ...
## $ drv : chr "f" "f" "f" "f" ...
## $ cty : int 18 21 20 21 16 18 18 18 16 20 ...
## $ hwy : int 29 29 31 30 26 26 27 26 25 28 ...
## $ fl : chr "p" "p" "p" "p" ...
## $ class : chr "compact" "compact" "compact" "compact" ...summary(mpg)## manufacturer model displ year
## Length:234 Length:234 Min. :1.600 Min. :1999
## Class :character Class :character 1st Qu.:2.400 1st Qu.:1999
## Mode :character Mode :character Median :3.300 Median :2004
## Mean :3.472 Mean :2004
## 3rd Qu.:4.600 3rd Qu.:2008
## Max. :7.000 Max. :2008
## cyl trans drv cty
## Min. :4.000 Length:234 Length:234 Min. : 9.00
## 1st Qu.:4.000 Class :character Class :character 1st Qu.:14.00
## Median :6.000 Mode :character Mode :character Median :17.00
## Mean :5.889 Mean :16.86
## 3rd Qu.:8.000 3rd Qu.:19.00
## Max. :8.000 Max. :35.00
## hwy fl class
## Min. :12.00 Length:234 Length:234
## 1st Qu.:18.00 Class :character Class :character
## Median :24.00 Mode :character Mode :character
## Mean :23.44
## 3rd Qu.:27.00
## Max. :44.00“The greatest value of a picture is when it forces us to notice what we never expected to see.” — John Tukey
可映射的图形属性
- color
- size
- shape
- alpha
+加号必须放在一句的末尾而不是下一句的开始。
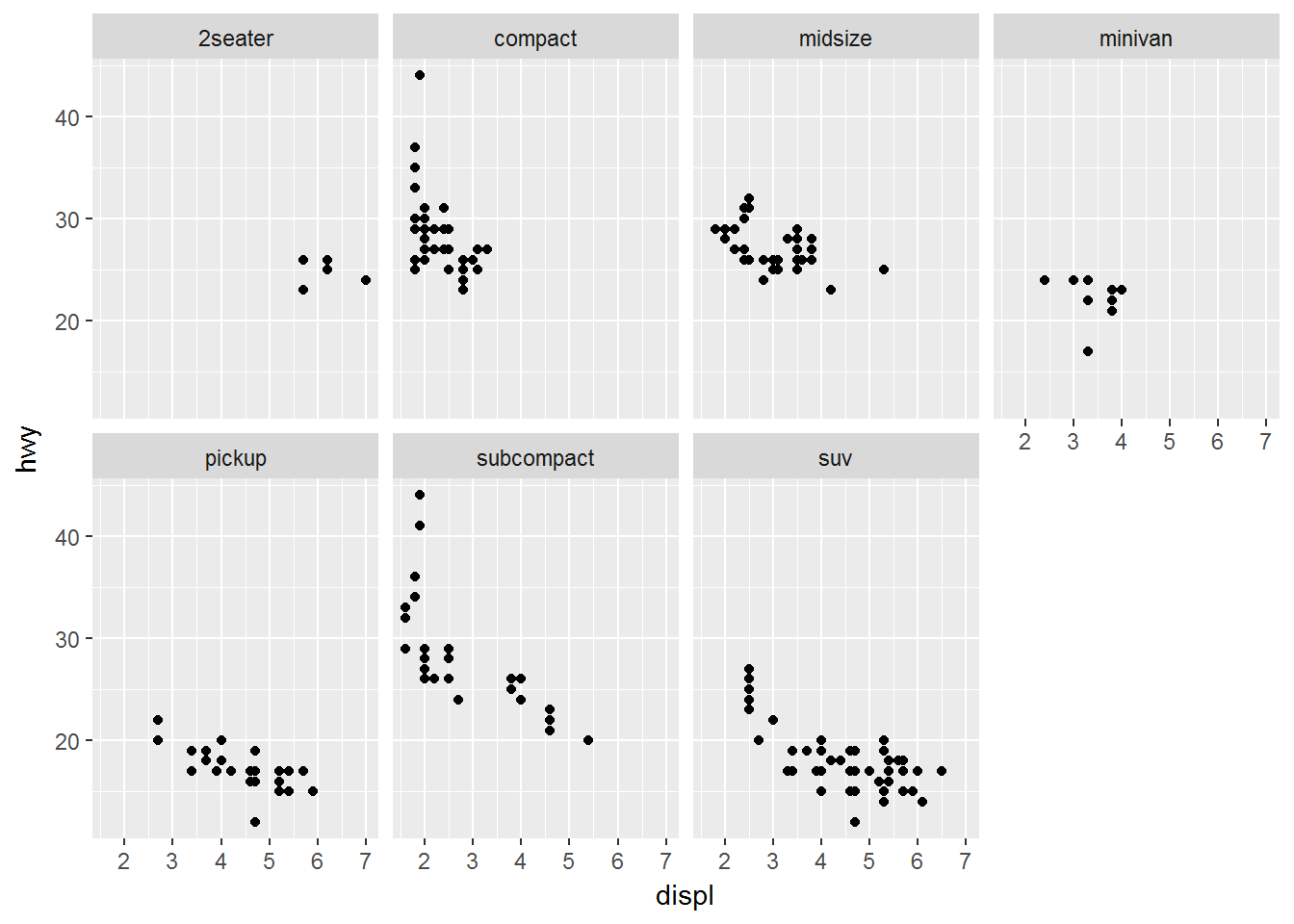
分面
对分类数据很有用
单一变量的分面:facet_wrap()
ggplot(data = mpg) +
geom_point(mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
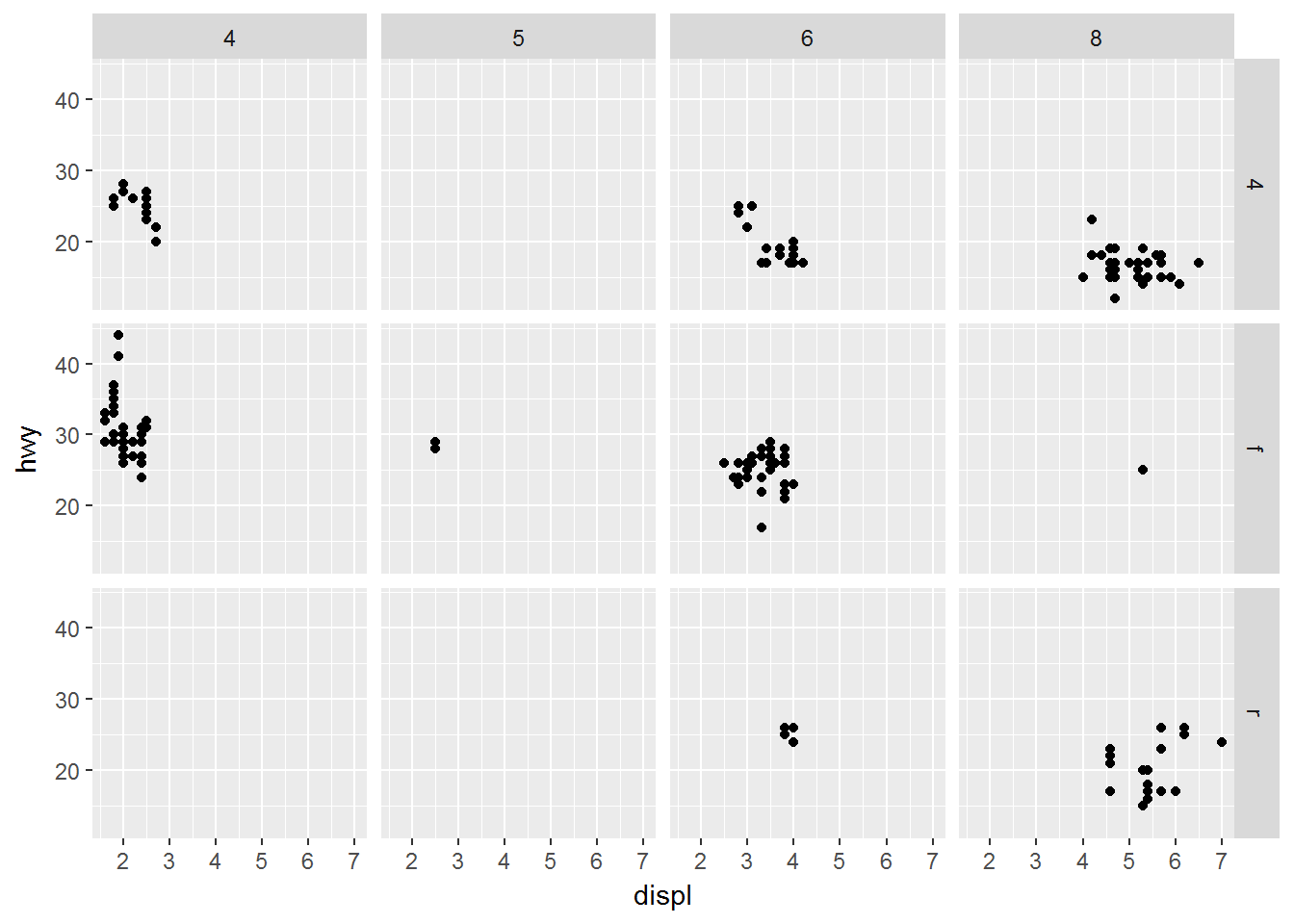
facet_wrap(~ class, nrow = 2)多变量分面:facet_grid()
ggplot(data = mpg) +
geom_point(mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
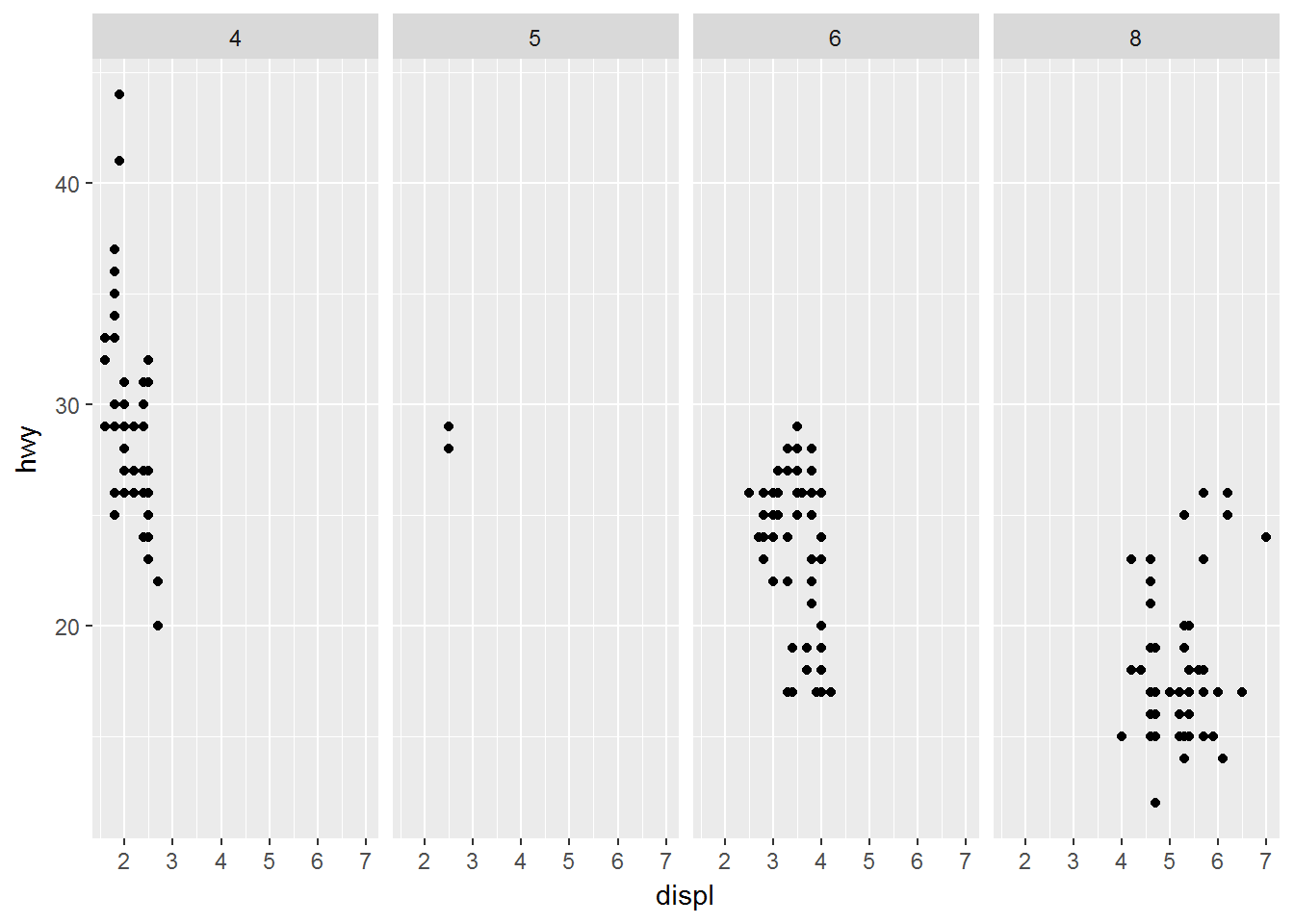
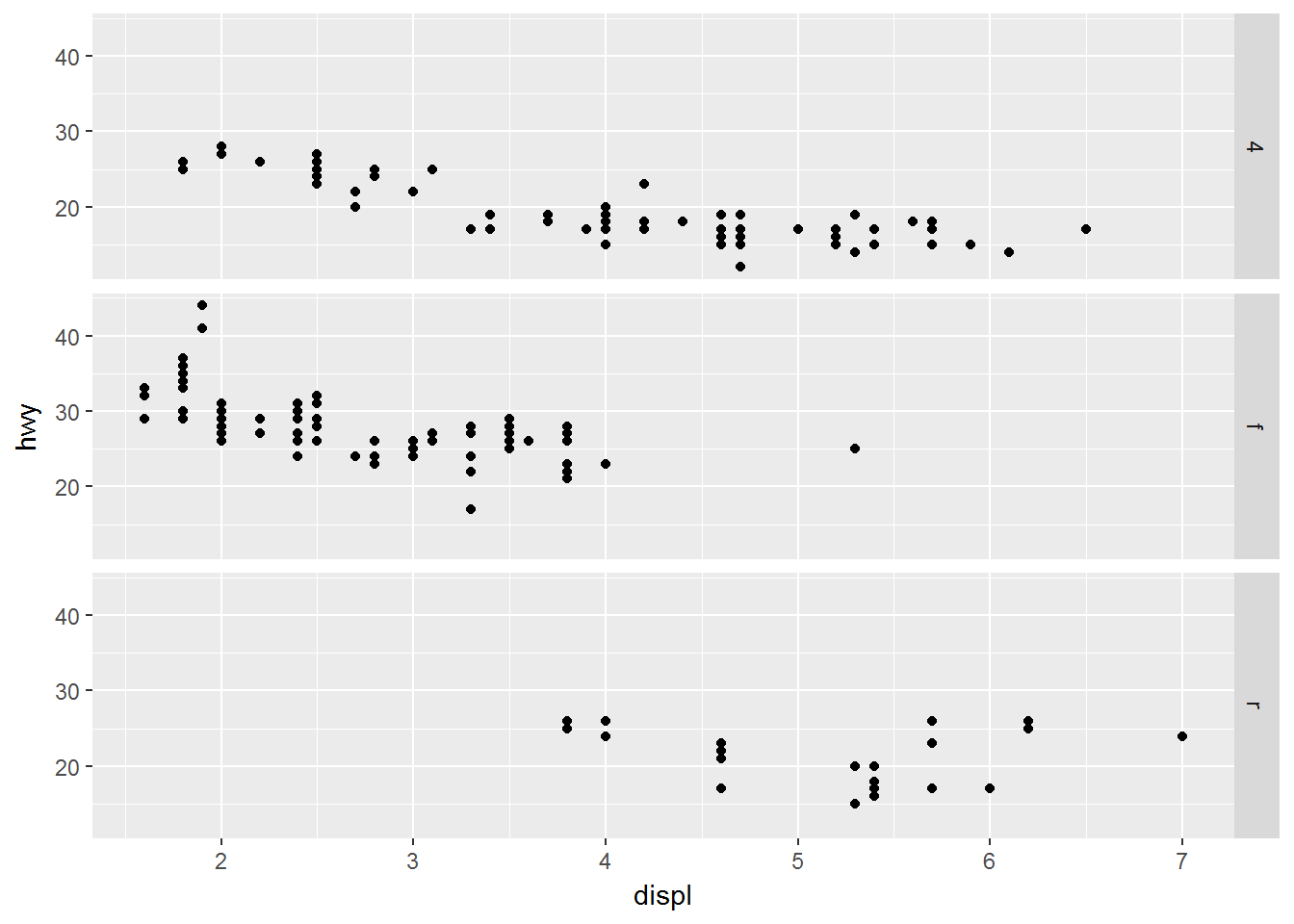
facet_grid(drv ~ cyl)ggplot(data = mpg) +
geom_point(mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
facet_grid(. ~ cyl)ggplot(data = mpg) +
geom_point(mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
facet_grid(drv ~ .)图形类型
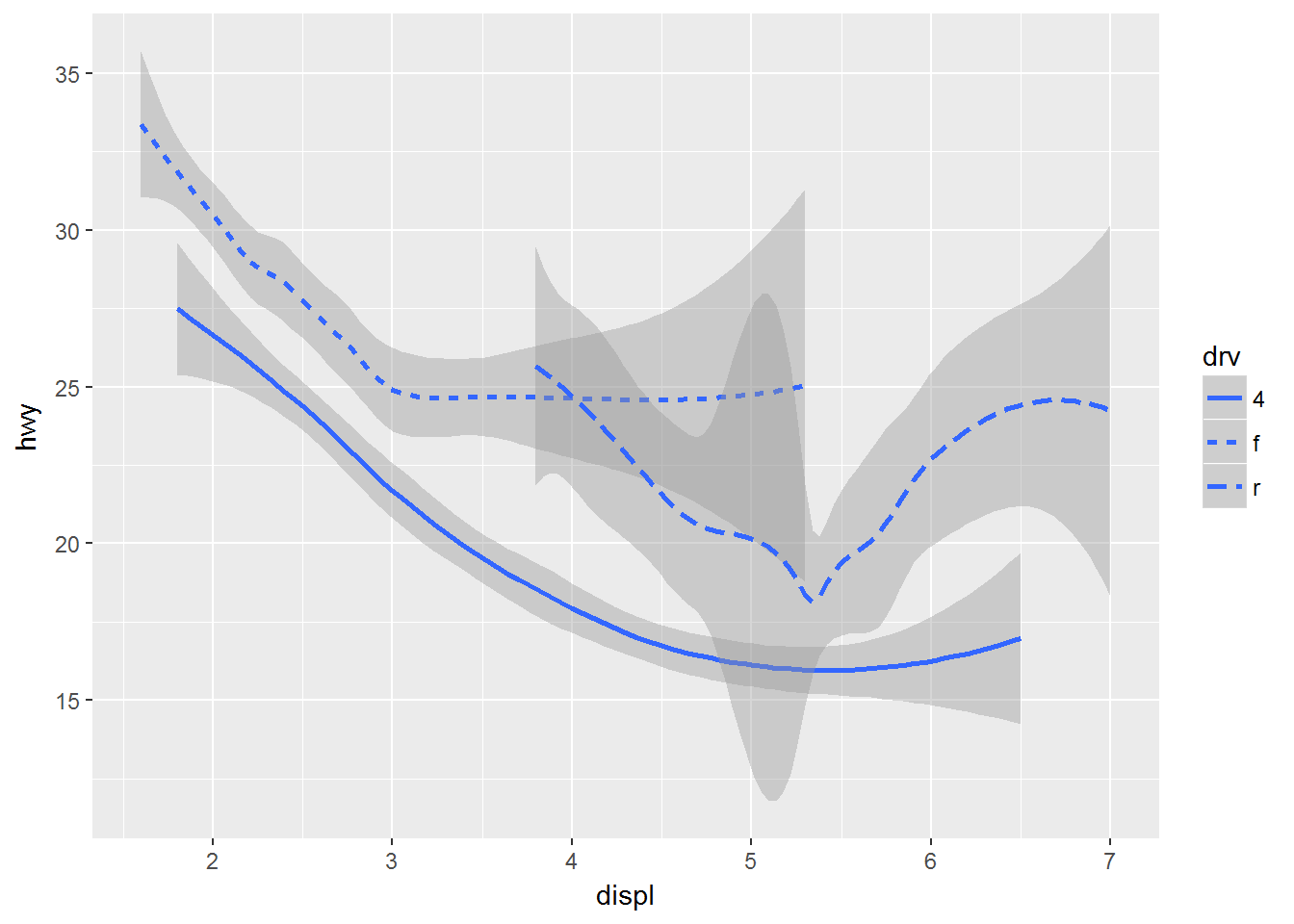
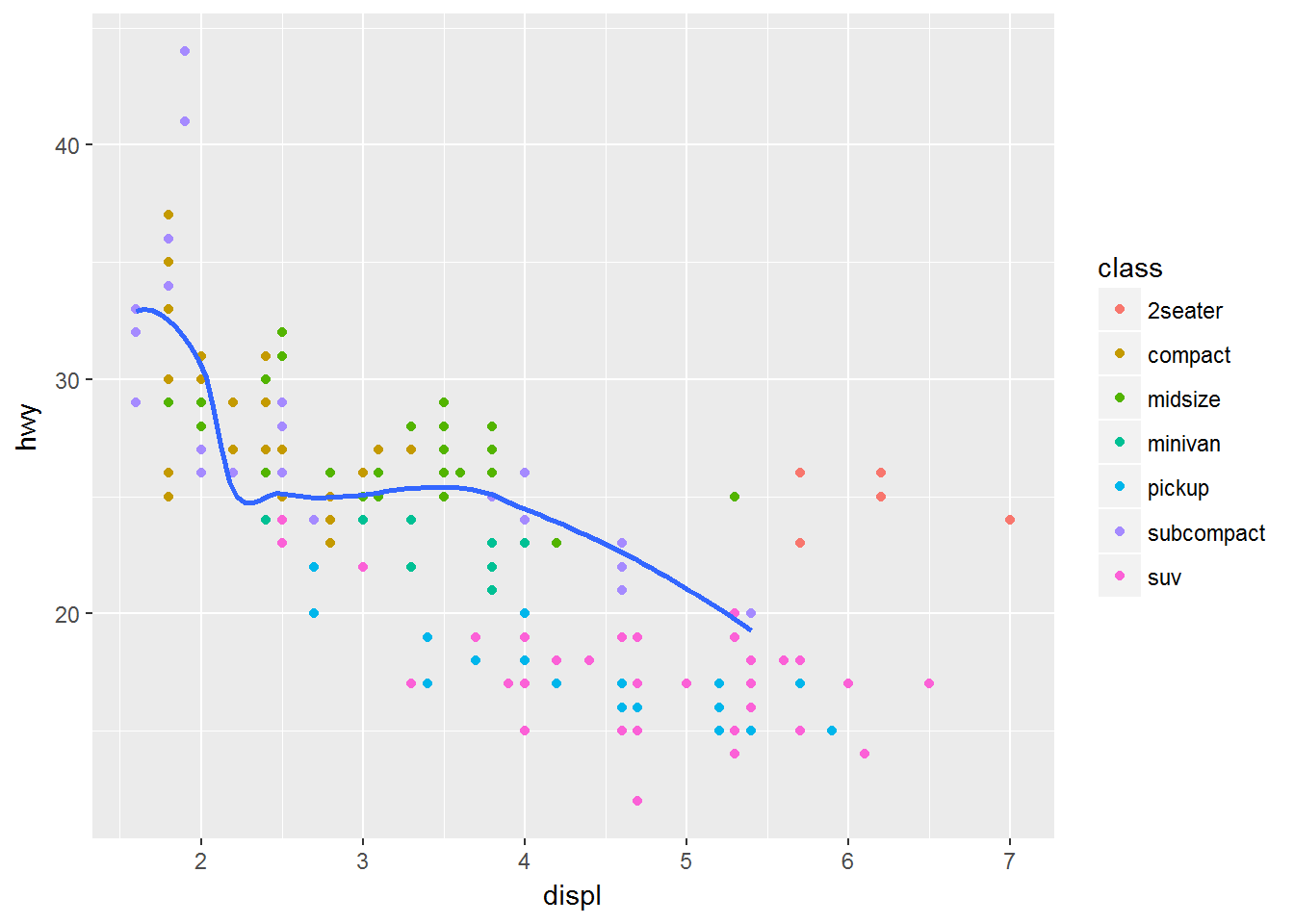
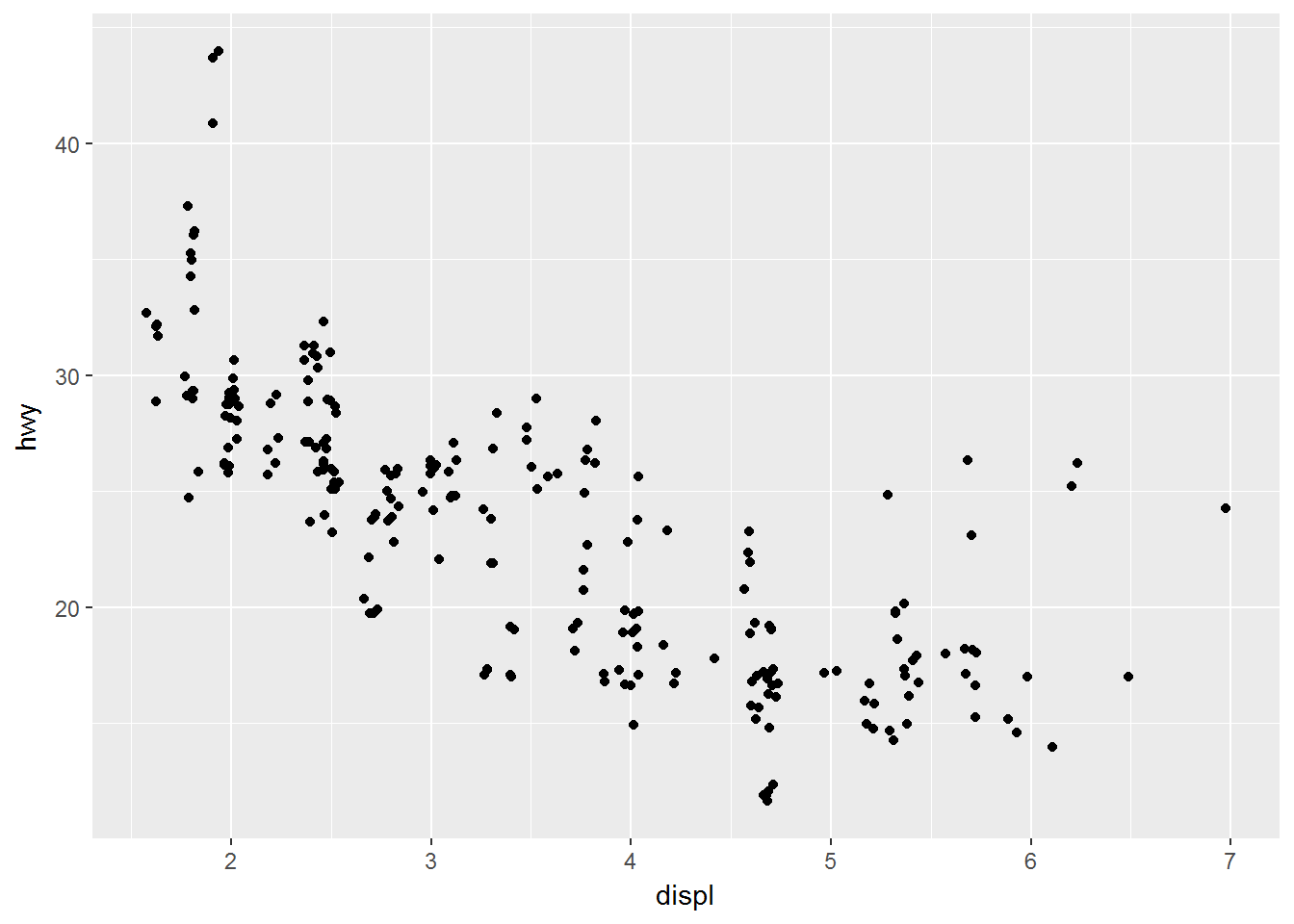
ggplot(data = mpg) +
geom_smooth(mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy, linetype = drv))## `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess'多个图形
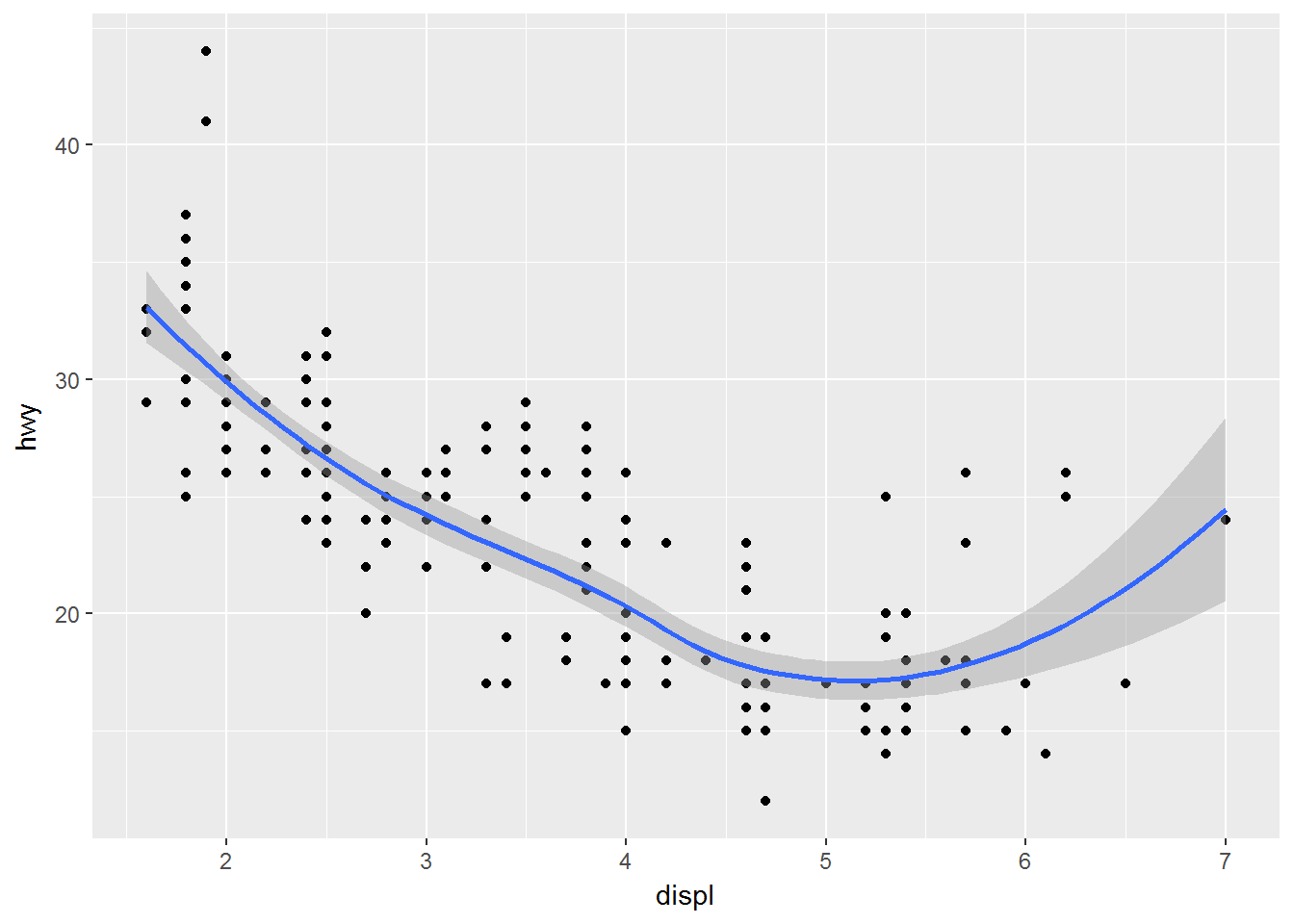
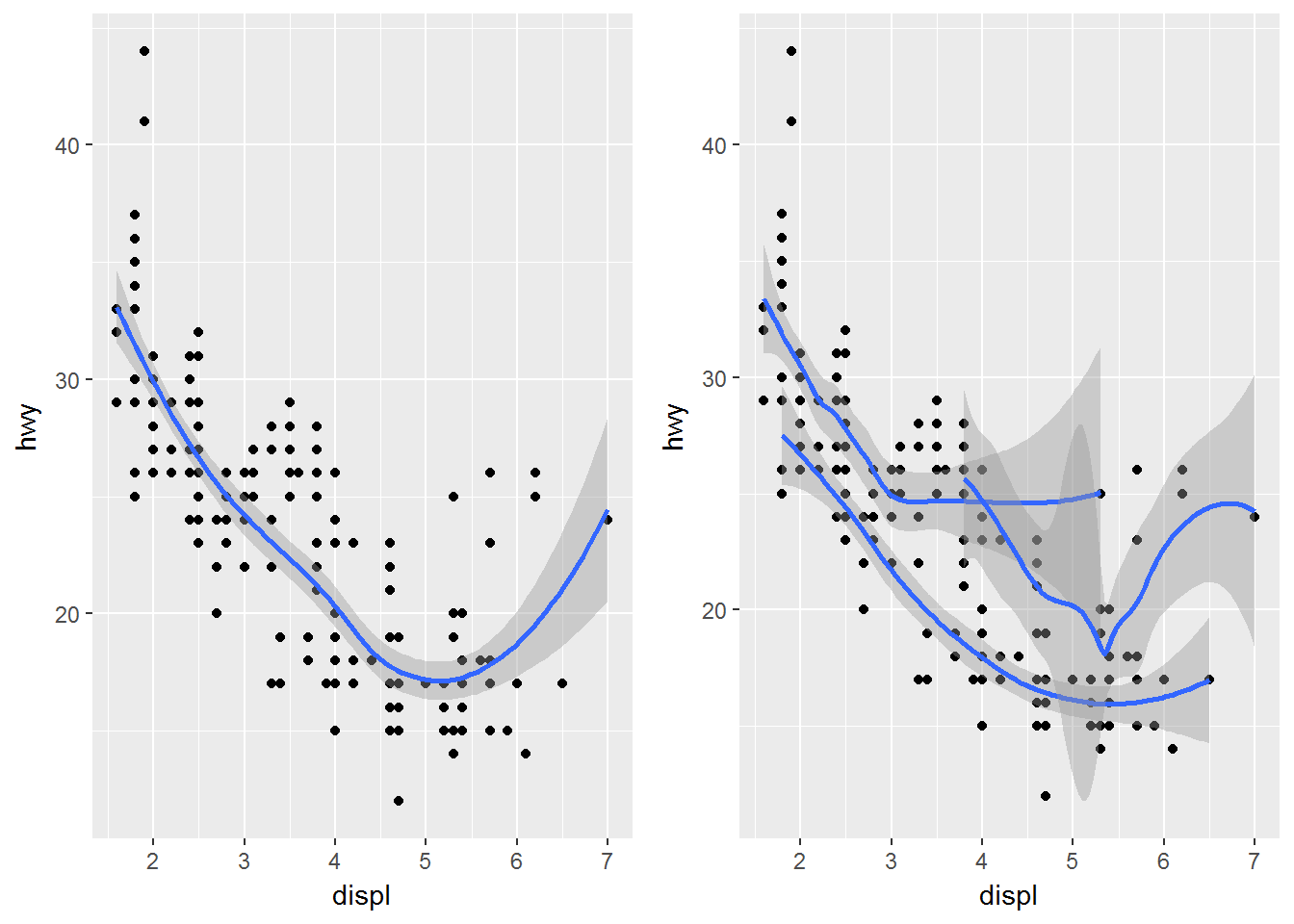
ggplot(data = mpg) +
geom_point(mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
geom_smooth(mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy))## `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess'避免重复的写法:
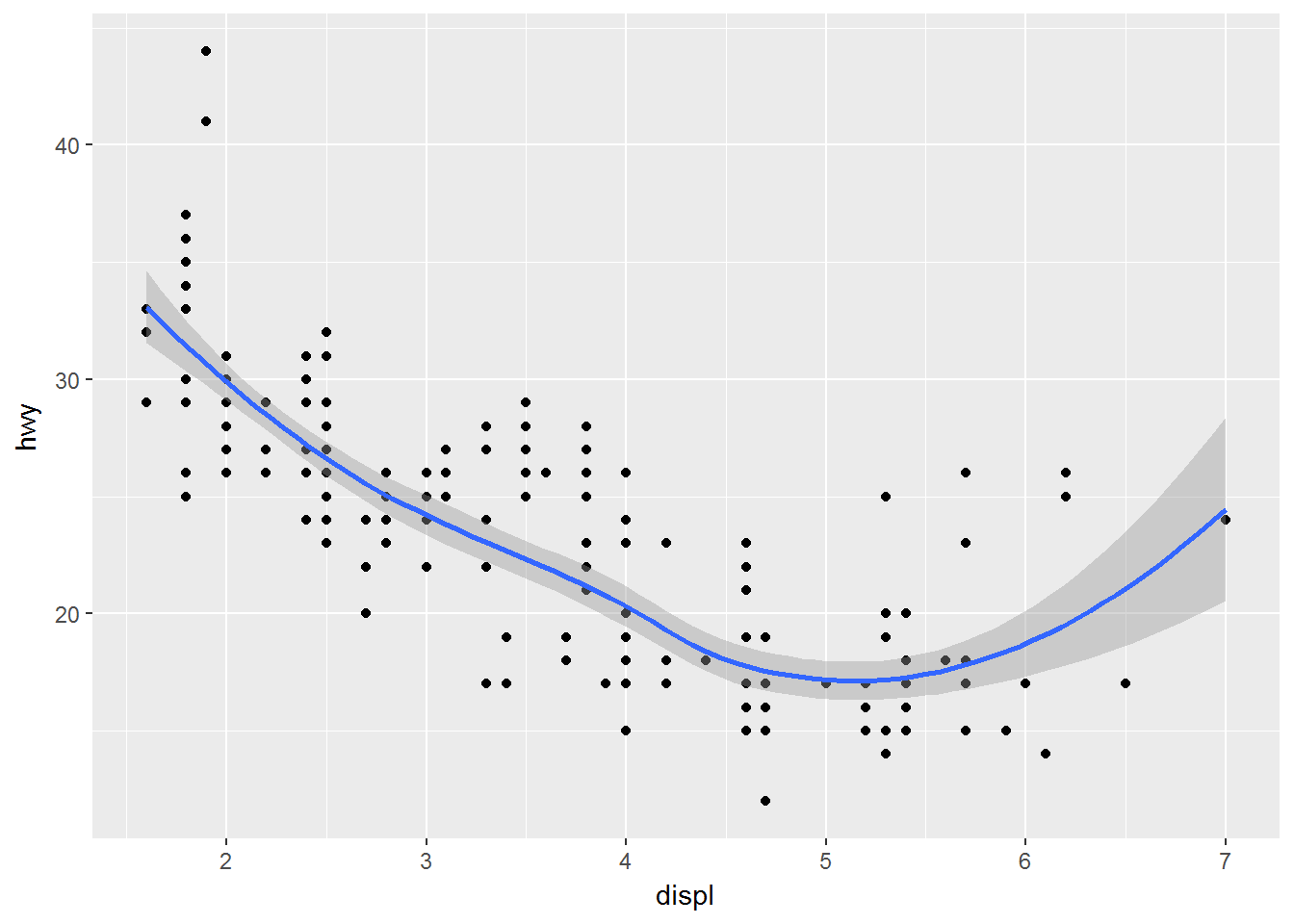
ggplot(data = mpg, mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth()## `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess'映射的重写
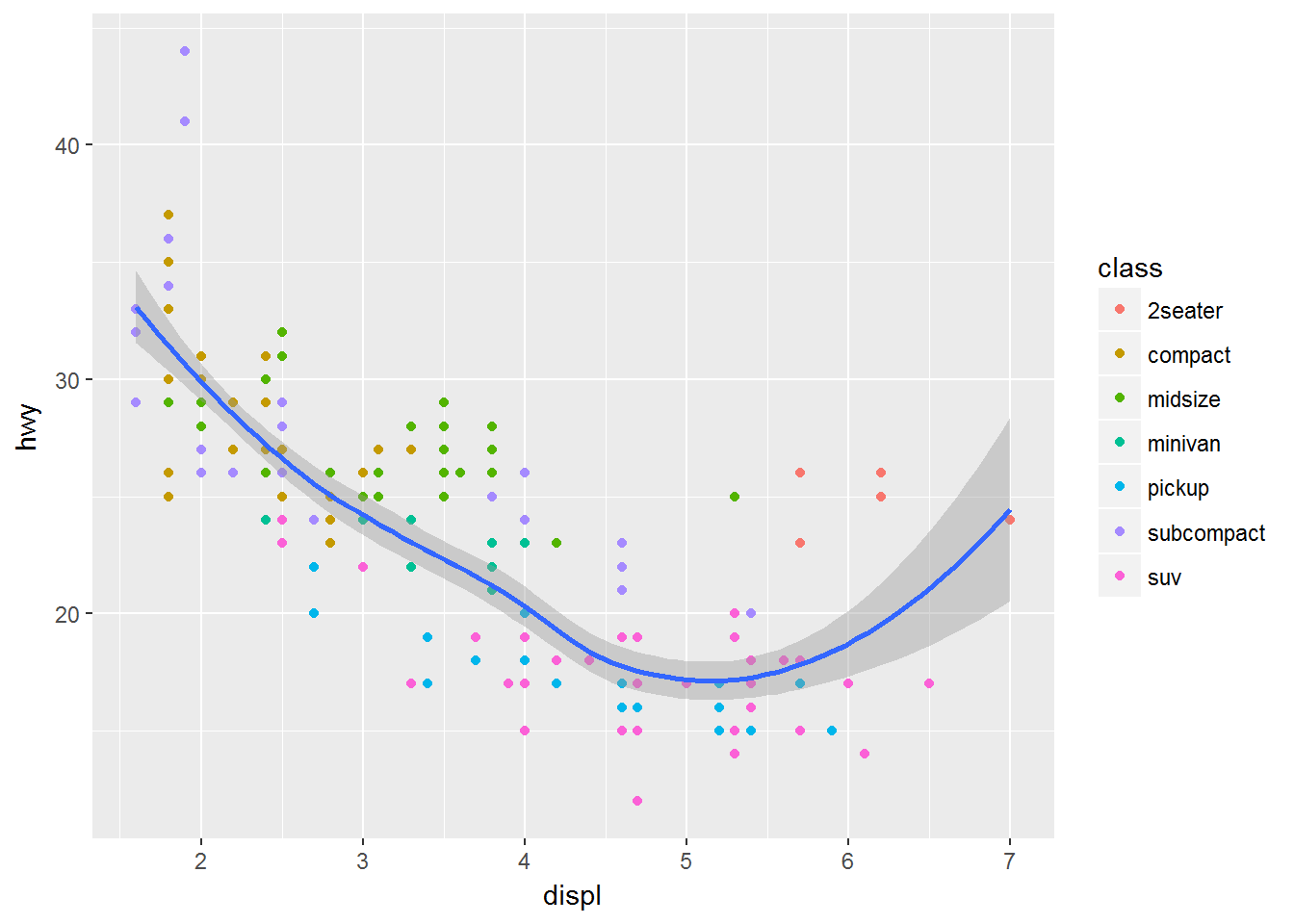
ggplot(data = mpg, mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
geom_point(mapping = aes(color = class)) +
geom_smooth()## `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess'甚至数据也能重写
ggplot(data = mpg, mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy)) +
geom_point(mapping = aes(color = class)) +
geom_smooth(data = filter(mpg, class == "subcompact"), se = FALSE)## `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess'p1 <- ggplot(mpg,aes(x=displ,y=hwy))+
geom_point()+
geom_smooth()
p2 <- ggplot(mpg,aes(x=displ,y=hwy))+
geom_point()+
geom_smooth(aes(group=drv))
usefulr::multiplot(p1,p2,cols = 2)## `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess'
## `geom_smooth()` using method = 'loess'数学变换
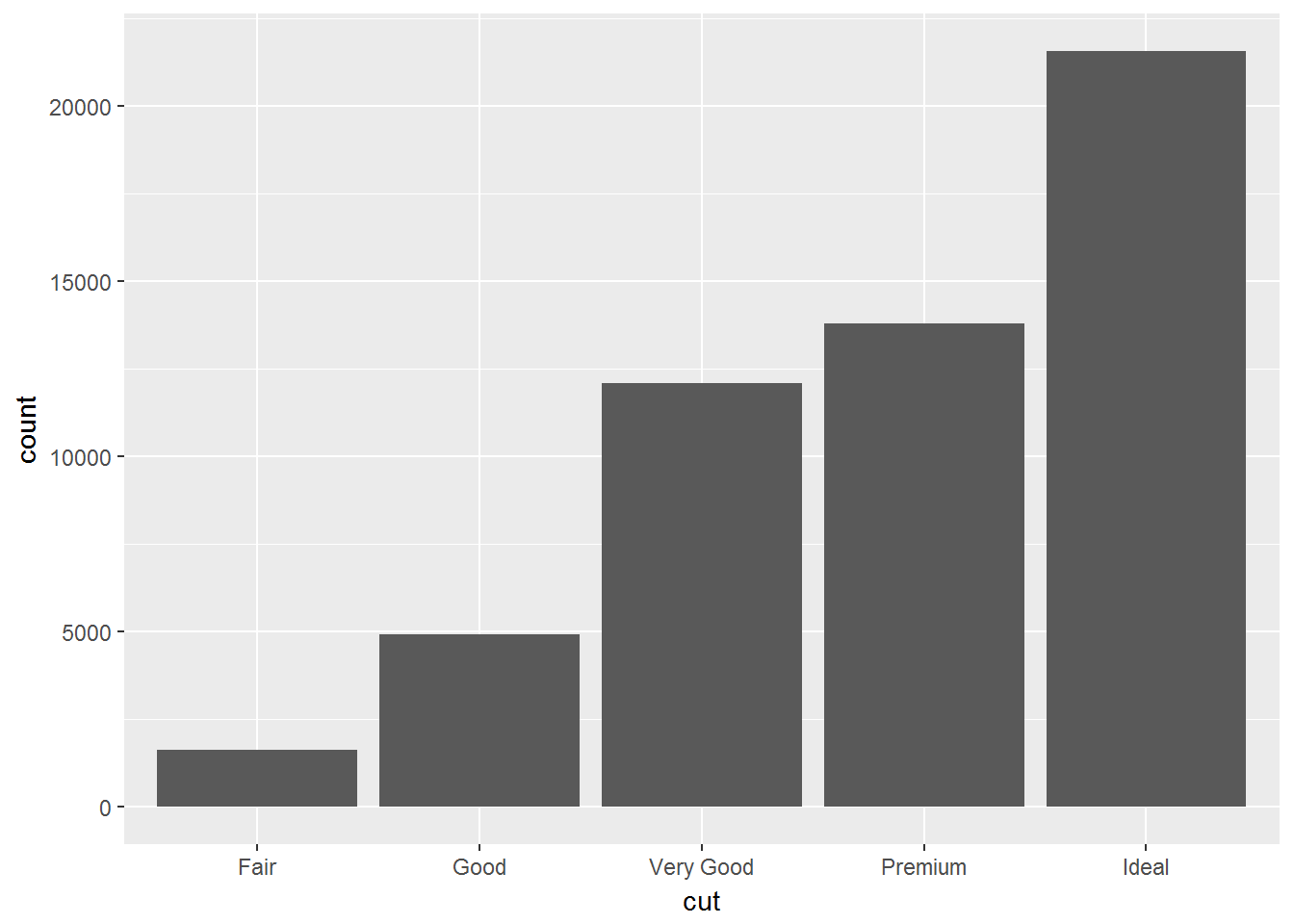
ggplot(data = diamonds) +
geom_bar(mapping = aes(x = cut))- bar charts, histograms, and frequency polygons bin your data and then plot bin counts, the number of points that fall in each bin.
- smoothers fit a model to your data and then plot predictions from the model.
- boxplots compute a robust summary of the distribution and then display a specially formatted box.
数学变换和图形的关系:
Every geom has a default stat; and every stat has a default geom.
更改图形对应的数学变换:
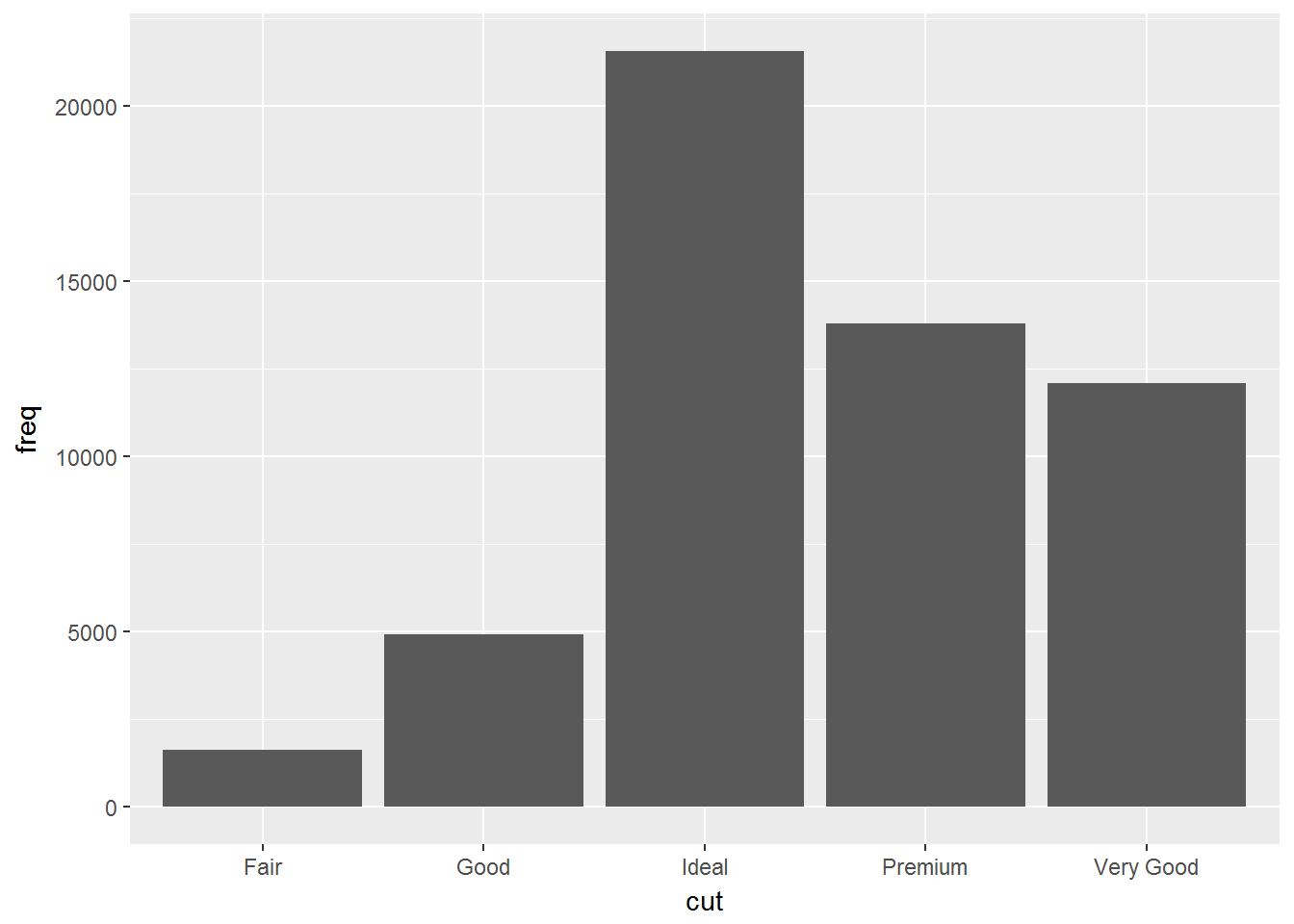
demo <- tribble(
~cut, ~freq,
"Fair", 1610,
"Good", 4906,
"Very Good", 12082,
"Premium", 13791,
"Ideal", 21551
)
ggplot(data = demo) +
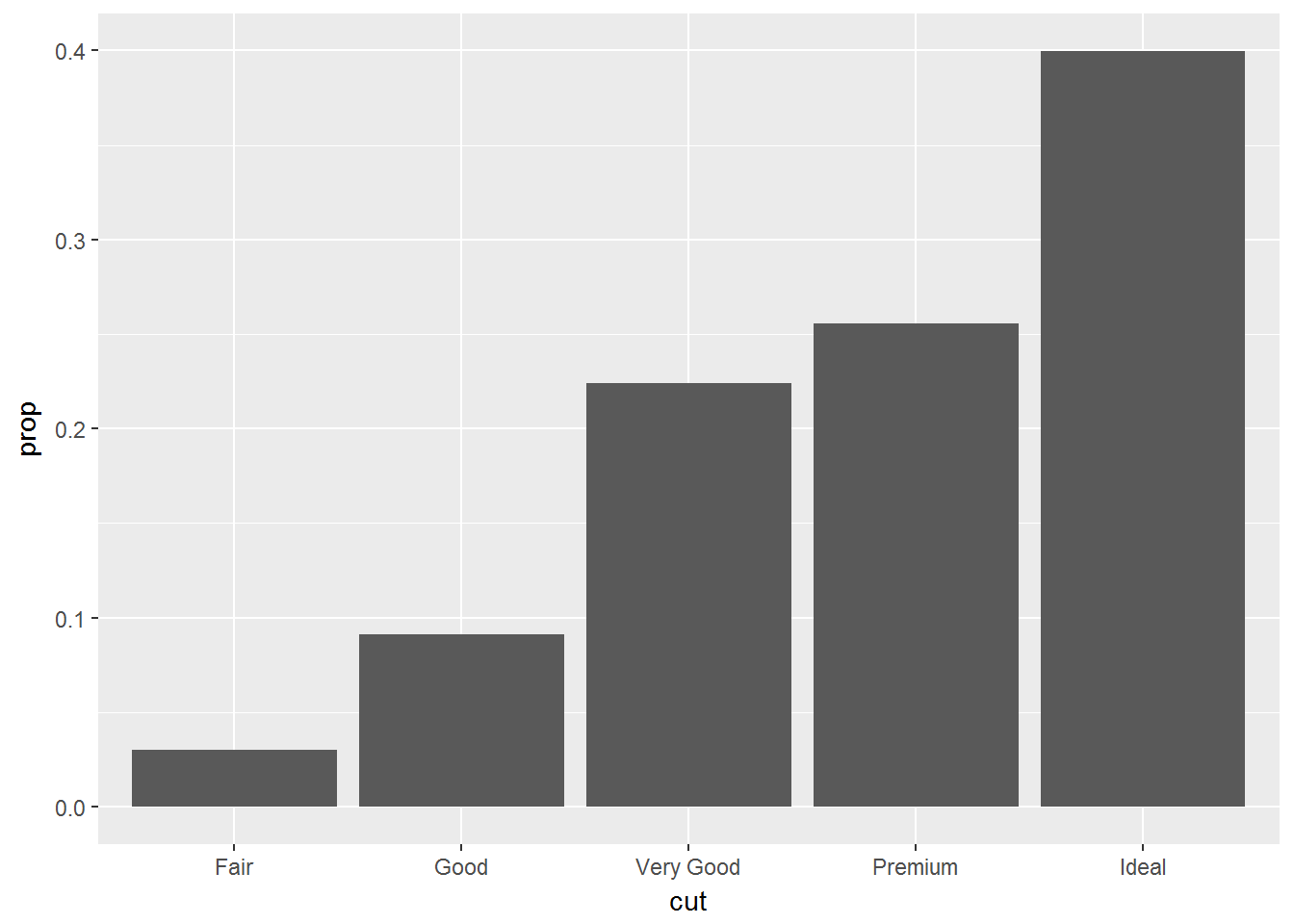
geom_bar(mapping = aes(x = cut, y = freq), stat = "identity")ggplot(data = diamonds) +
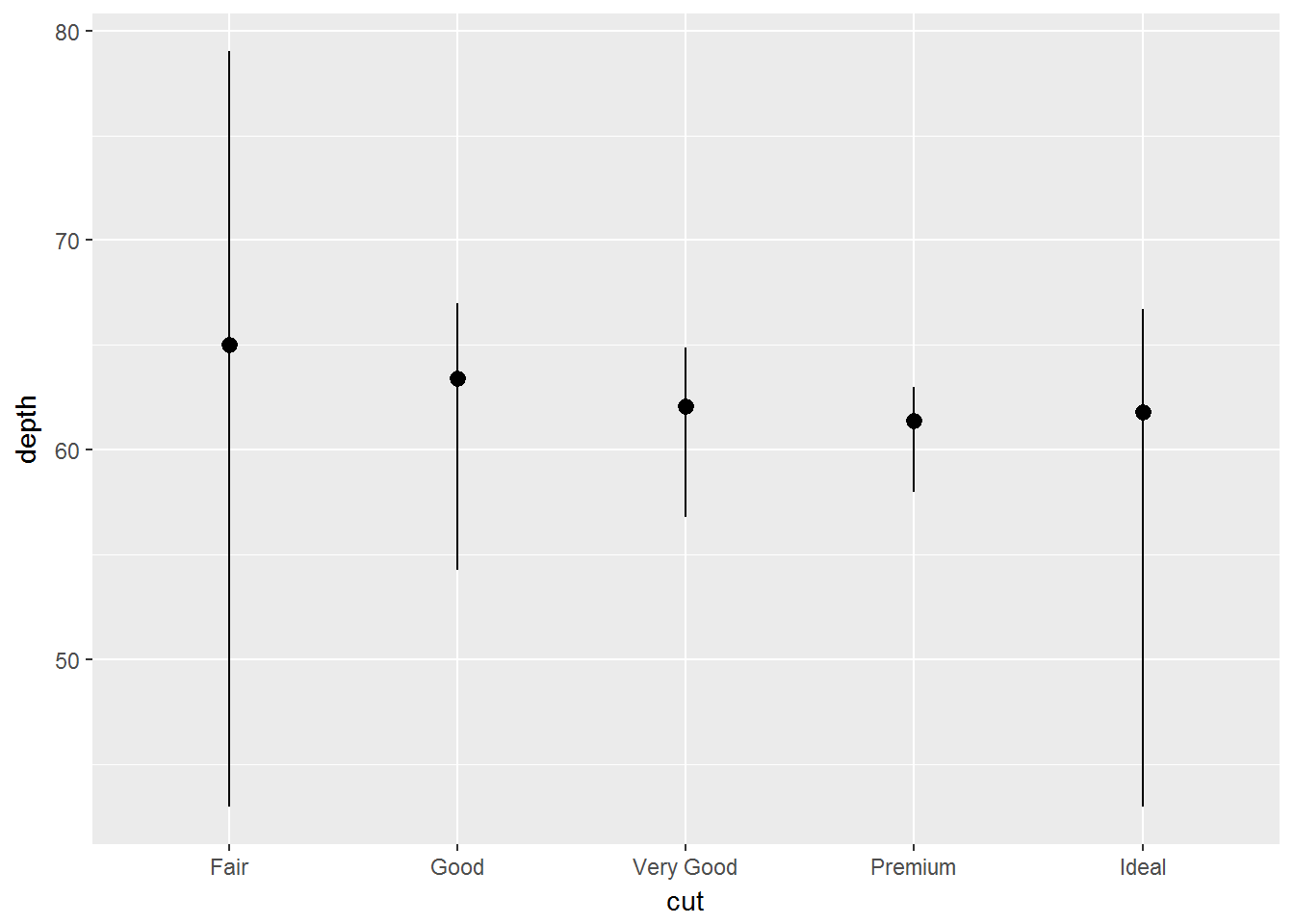
geom_bar(mapping = aes(x = cut, y = ..prop.., group = 1))ggplot(data = diamonds) +
stat_summary(
mapping = aes(x = cut, y = depth),
fun.ymin = min,
fun.ymax = max,
fun.y = median
)位置调整
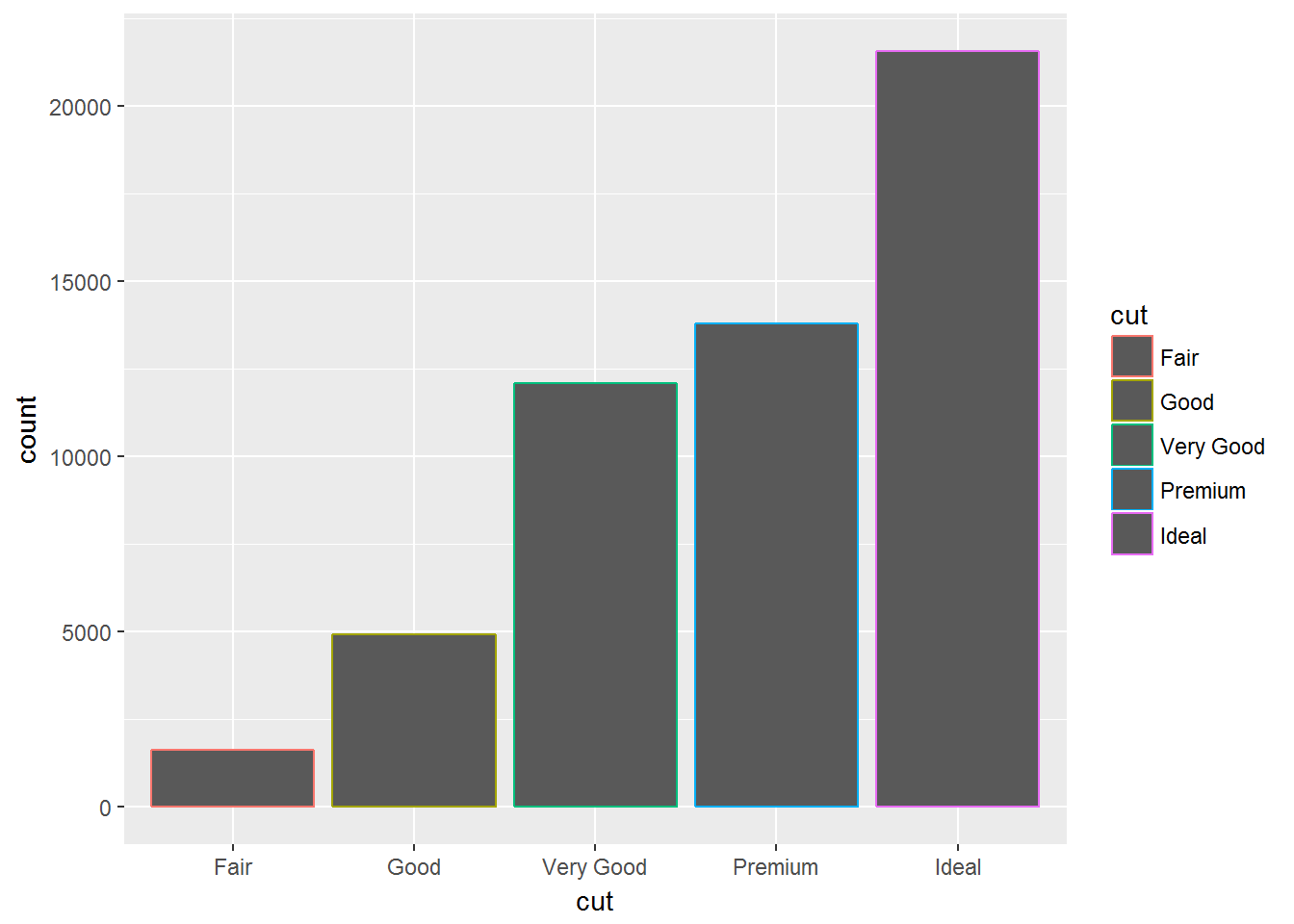
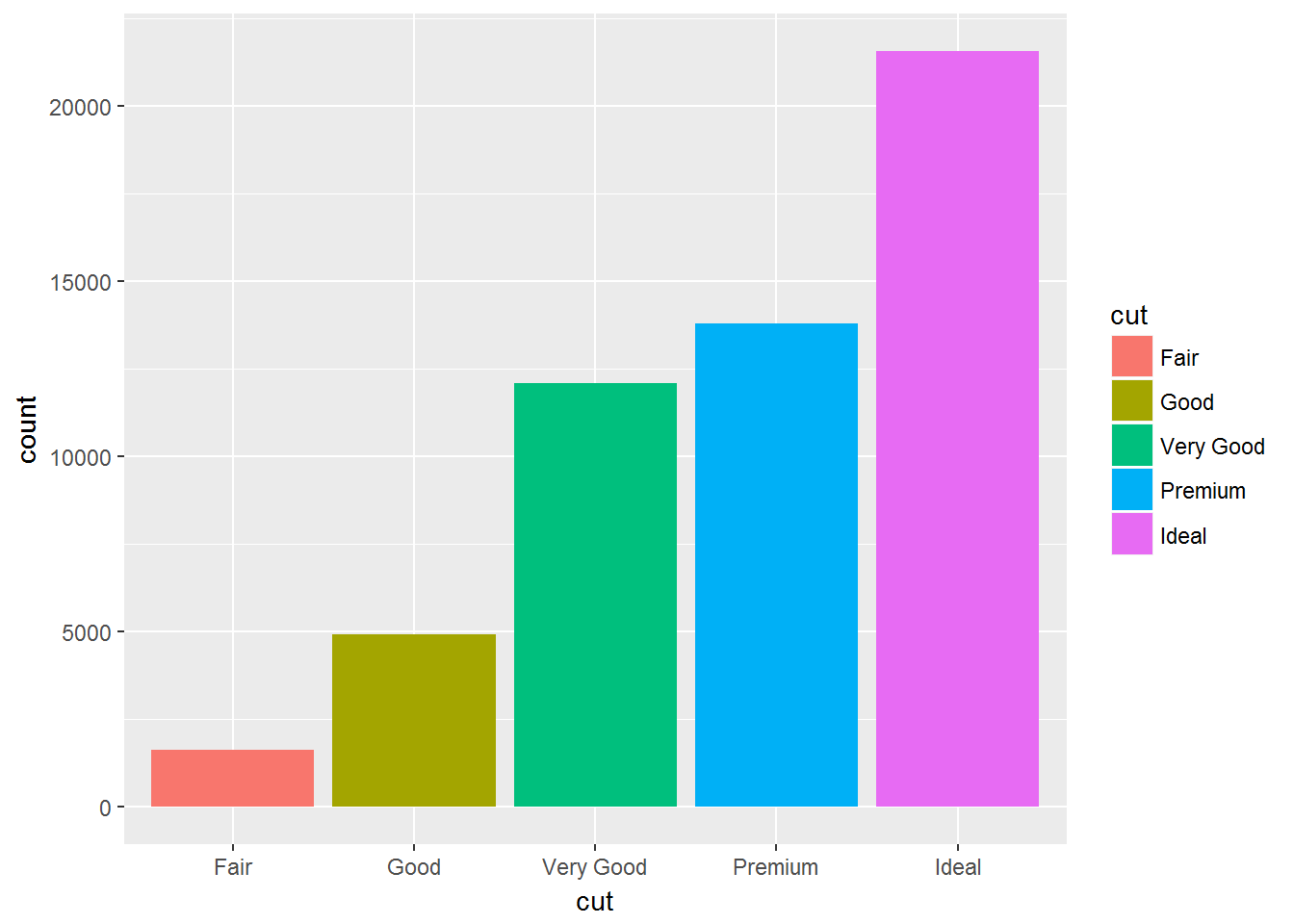
ggplot(data = diamonds) +
geom_bar(mapping = aes(x = cut, colour = cut))ggplot(data = diamonds) +
geom_bar(mapping = aes(x = cut, fill = cut))ggplot(data = diamonds) +
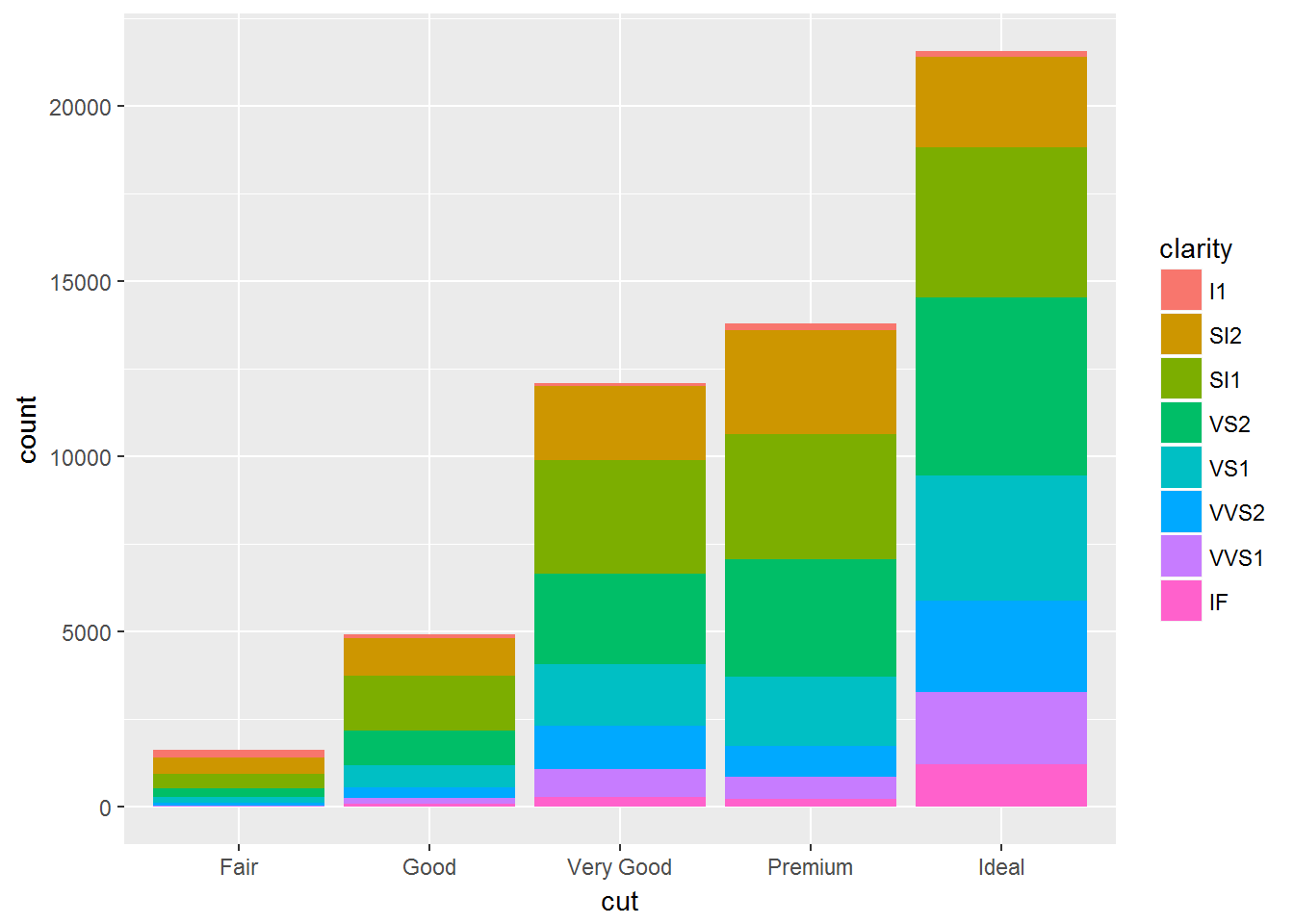
geom_bar(mapping = aes(x = cut, fill = clarity))位置调整的四种选择:
- stacked
- identity
- dodge
- fill
- jitter
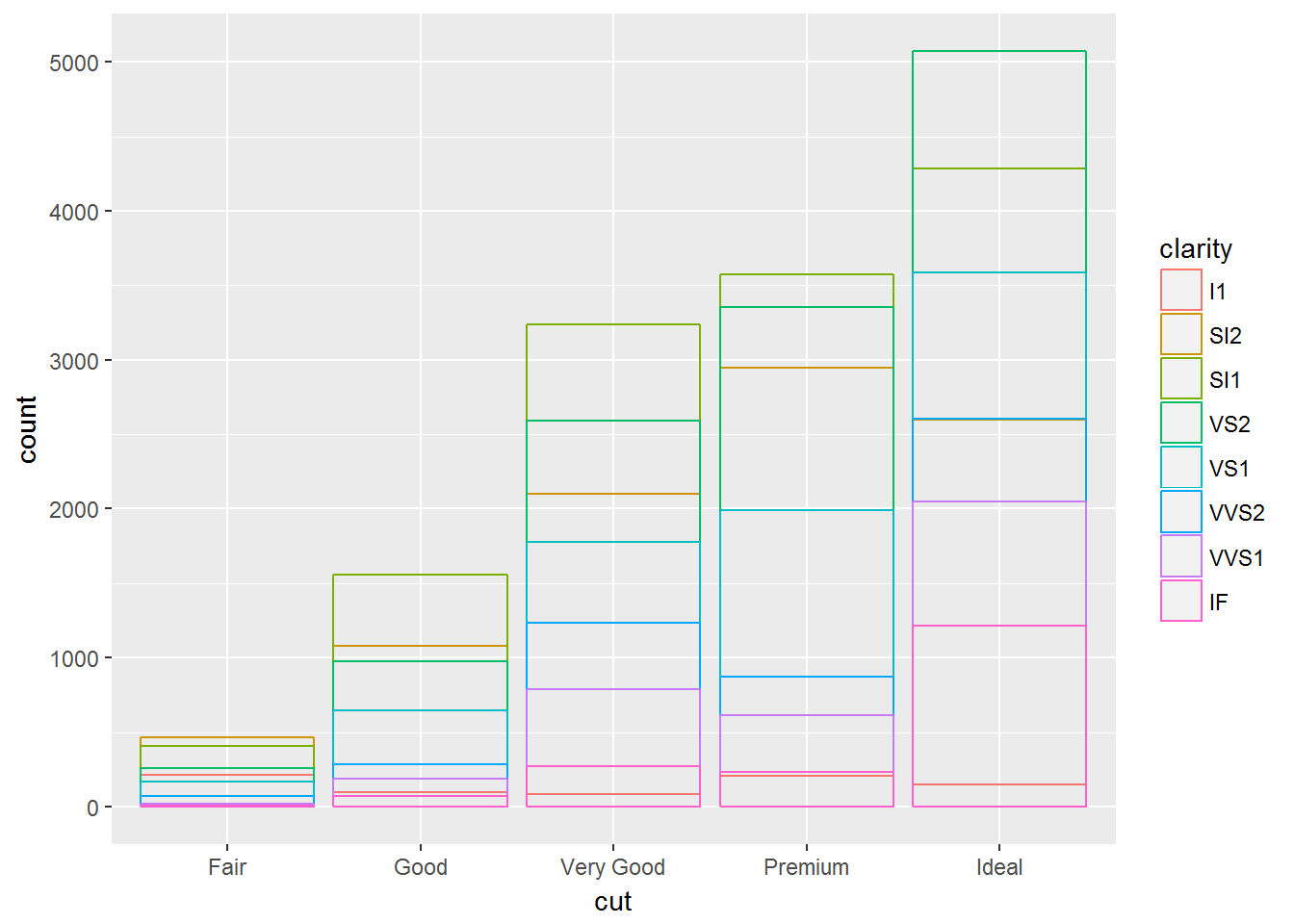
identity适合展现二维数据
ggplot(data = diamonds, mapping = aes(x = cut, colour = clarity)) +
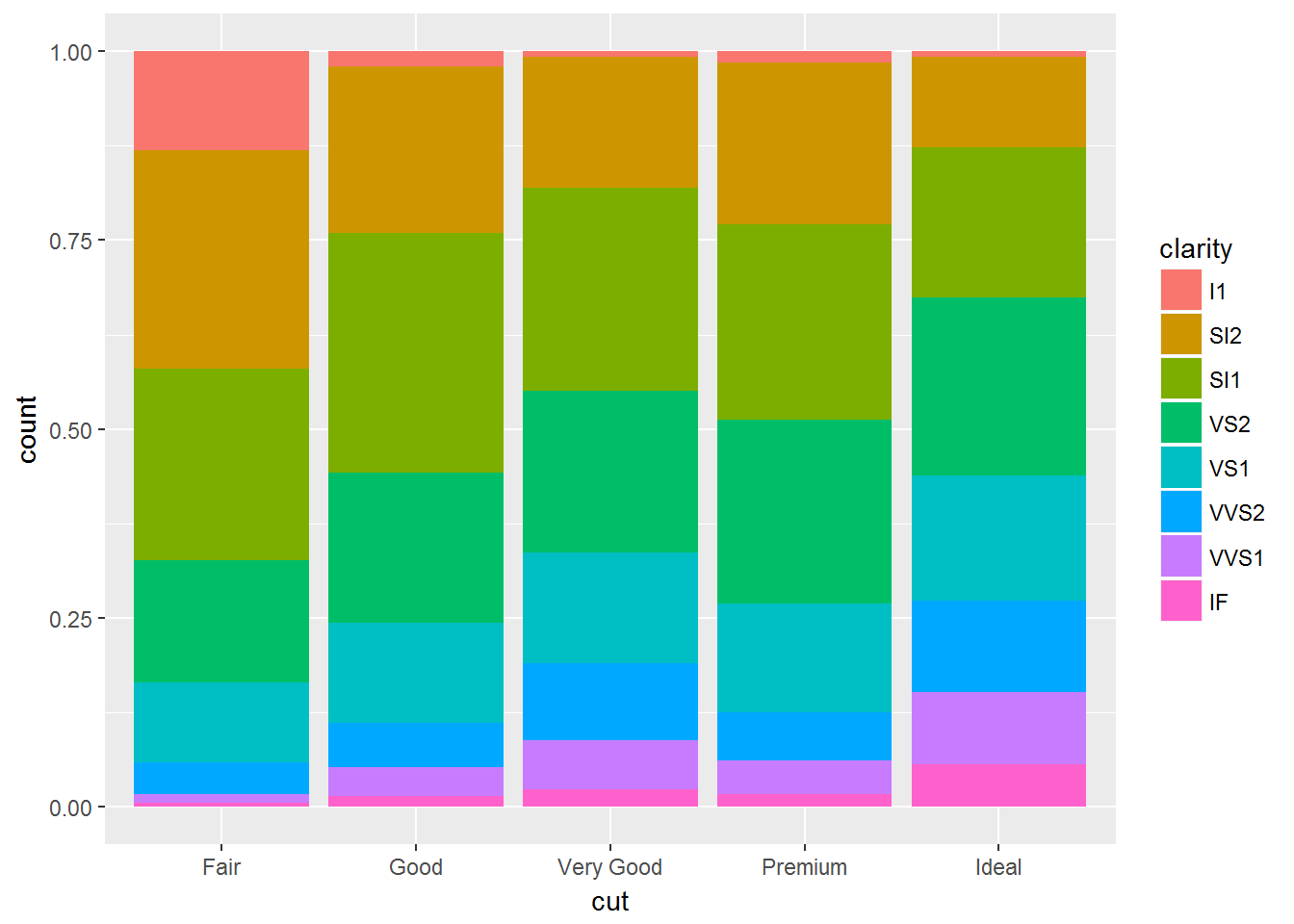
geom_bar(fill = NA, position = "identity")fill适合展现百分比
ggplot(data = diamonds) +
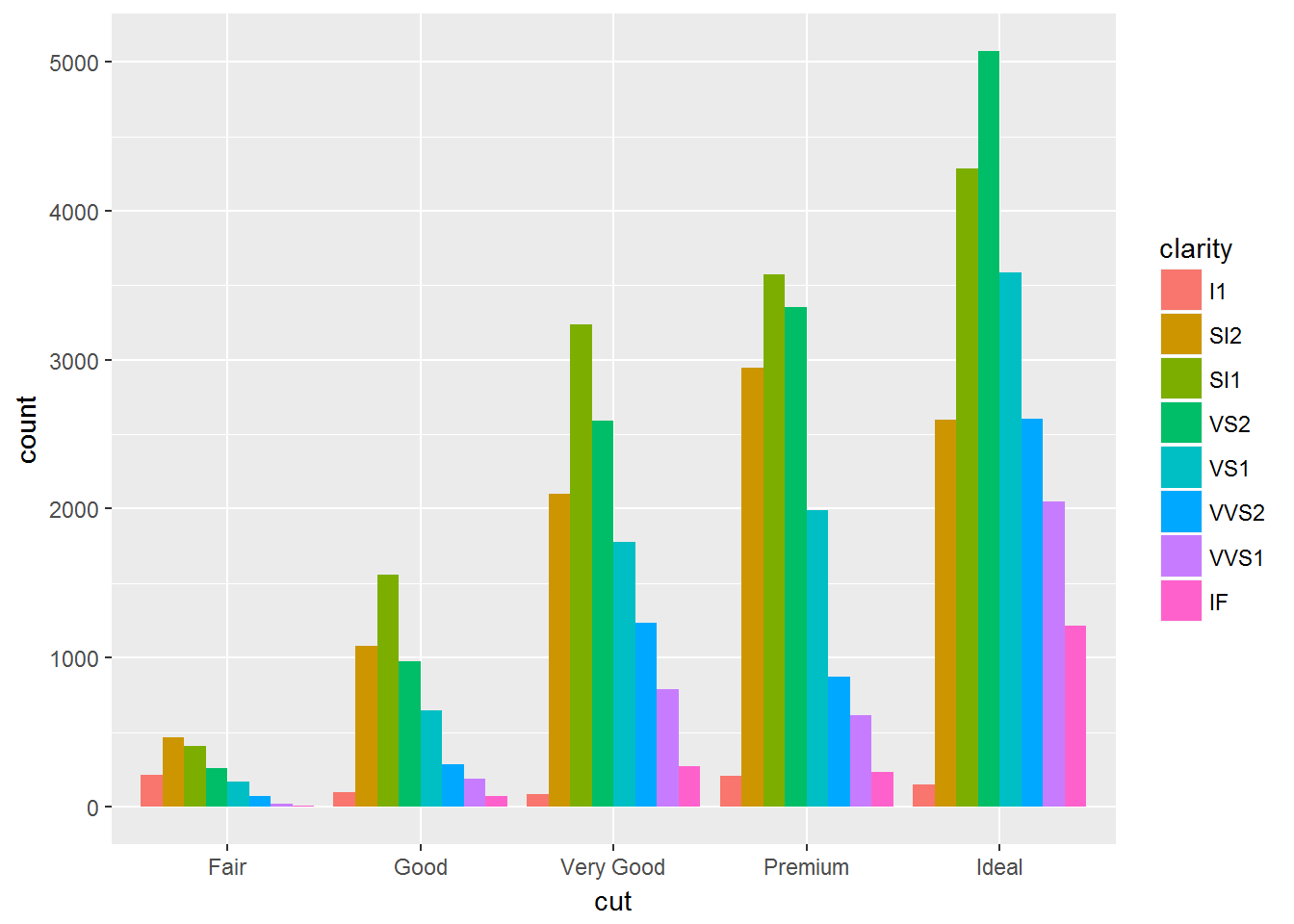
geom_bar(mapping = aes(x = cut, fill = clarity), position = "fill")dodge适合展现个体差异
ggplot(data = diamonds) +
geom_bar(mapping = aes(x = cut, fill = clarity), position = "dodge")jitter适合展现重叠在一起的大量点,增加扰动
ggplot(data = mpg) +
geom_point(mapping = aes(x = displ, y = hwy), position = "jitter")坐标系统
翻转坐标
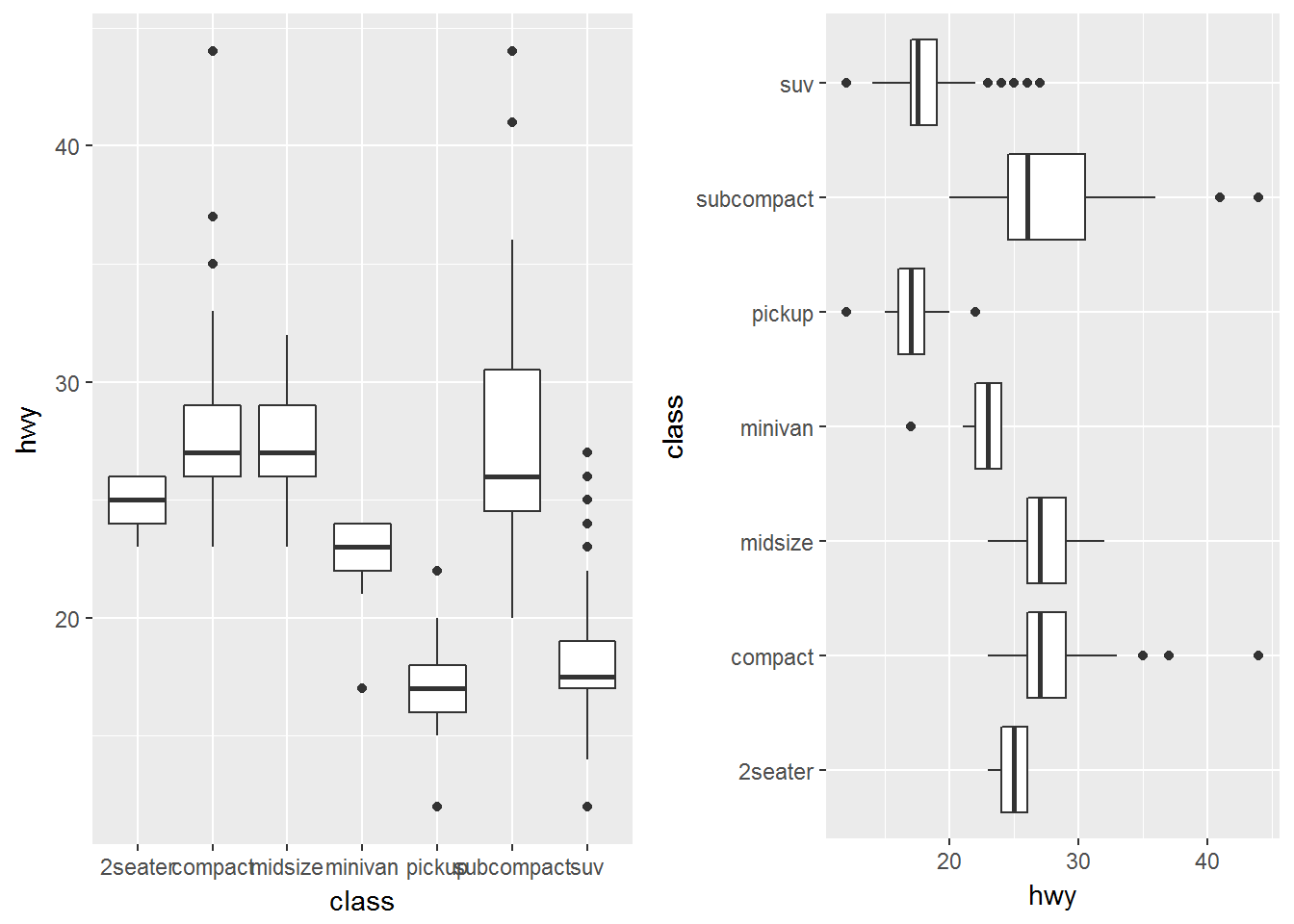
p1 <- ggplot(data = mpg, mapping = aes(x = class, y = hwy)) +
geom_boxplot()
p2 <- ggplot(data = mpg, mapping = aes(x = class, y = hwy)) +
geom_boxplot() +
coord_flip()
usefulr::multiplot(p1,p2,cols=2)极坐标
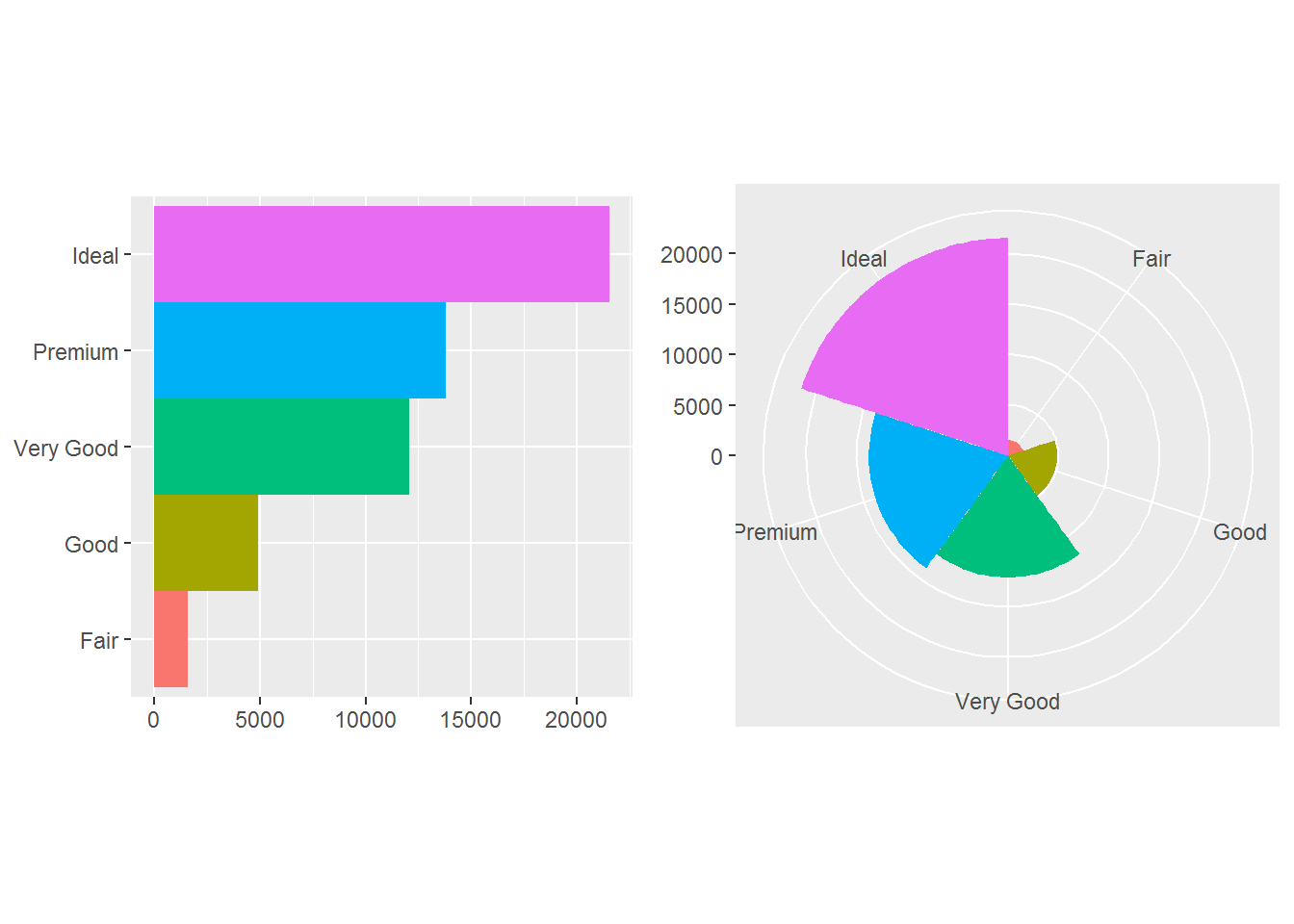
bar <- ggplot(data = diamonds) +
geom_bar(
mapping = aes(x = cut, fill = cut),
show.legend = FALSE,
width = 1
) +
theme(aspect.ratio = 1) +
labs(x = NULL, y = NULL)
p1 <- bar + coord_flip()
p2 <- bar + coord_polar()
usefulr::multiplot(p1,p2,cols=2)